Advertisement
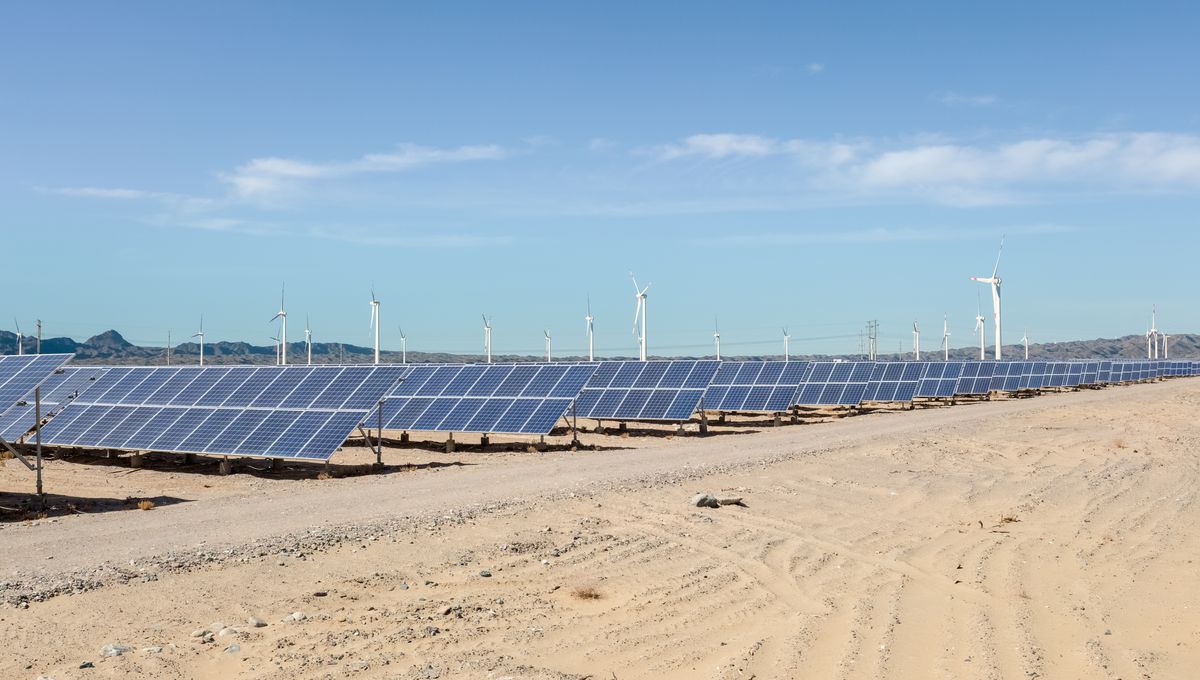
Nestled in the desert expanses of Ürümqi, the capital of the often-controversial Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China, a colossal 3.5-gigawatt-capacity plant is set to light up the world. This behemoth is projected to churn out a staggering 6.09 billion kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity annually. To put that into perspective, it’s enough to power countries like Cameroon or Laos, or meet the entire electrical needs of Vermont or Alaska.
This development is part of a broader wave of investment in renewable energy sweeping across China, a trend that the International Energy Agency (IEA) has hailed as “extraordinary”.
“In 2023, China commissioned as much solar PV as the entire world did in 2022,” the IEA highlighted in its Renewables 2023 report released earlier this year.
This is a beacon of hope for those of us who prefer a habitable world over a post-climate-apocalypse wasteland. Currently, China holds the dubious honor of being the largest contributor of carbon emissions from fossil fuels and industry. While this is largely due to its massive population – the US has a higher per capita impact – it still surpasses the combined emissions of the entire developed world.
However, recent indicators suggest that China’s carbon emissions may have reached their zenith. For the first time in 14 months, emission levels dipped in March, as reported by The Economist, citing an analysis by Carbon Brief. The same trend likely continued into April. While it’s premature to declare a definitive peak, experts are confident that China is on track to meet its stated goal of reaching peak emissions by 2030.
“By 2030 […] almost half of China’s electricity generation will come from renewable energy sources,” the IEA forecasts. This is largely due to China’s relentless pursuit of wind and solar farm development. In fact, even before this new solar mega-plant came online, the two largest operational facilities were already situated in western China.
The Xinjiang region, with its sparse population and abundant sun and wind, has become a hotbed for renewable energy production in China. This is despite its reputation as a rich source of oil and mineral resources.
Perhaps the scales will eventually tip in favor of renewable energy. After all, China has committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2060 – a goal that is unattainable without substantial investment in renewables. If recent developments and data are any indication, China might just be on track to achieve this ambitious target.
“This major strategic decision [reaching net-zero] is made based on our sense of responsibility to build a community with a shared future for mankind,” President Xi declared at a US-organized climate summit in 2021. “And our own need to secure sustainable development.”